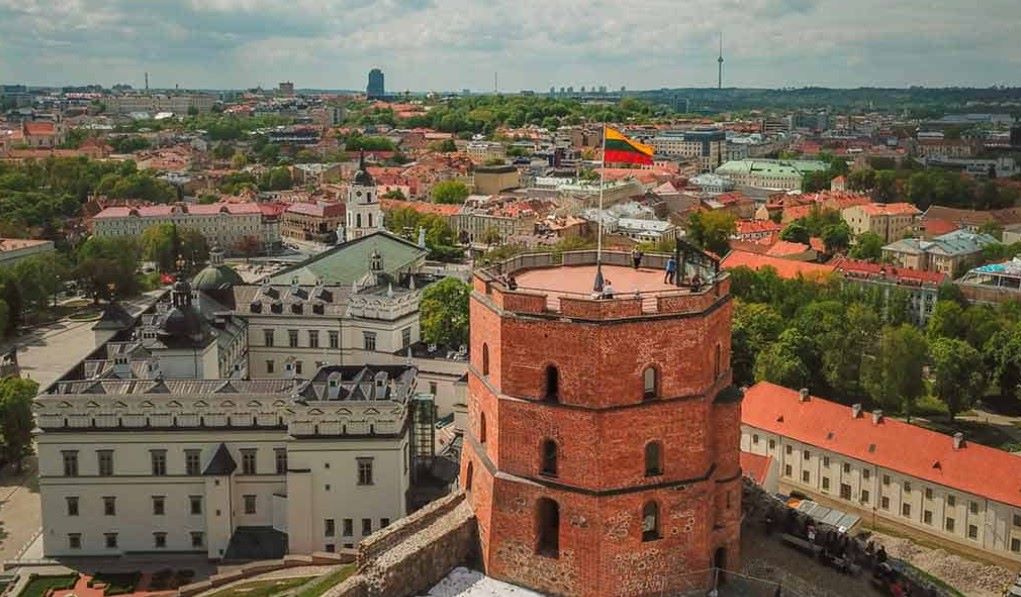
Economy
Lithuania’s economy exited the COVID-19-crisis successfully and was growing fast until early 2022, buoyed by rising exports and rapid integration into global value chains. However, with Russia’s aggression of Ukraine continuing and its consequences spreading, the outlook has darkened. Growth has slowed, and inflation has risen to some of the highest levels in the euro area, driven by high energy and food prices. The country cut all energy ties with Russia, relying on imports from other countries instead. The government supports the many Ukrainian refugees and helps households and firms weather the energy crisis. Structural unemployment and skills mismatch remain high, while poverty declines only slowly.
Foreign Direct Investment in Lithuania increased by 921.56 EUR Million in the fourth quarter of 2024. Foreign Direct Investment in Lithuania averaged 341.53 EUR Million from 2004 until 2024, reaching an all time high of 2582.14 EUR Million in the second quarter of 2020 and a record low of -610.08 EUR Million in the first quarter of 2016.
Further reform could help maintain economic resilience and cope with rising uncertainty. Reducing the scope of state-owned firms and improving their governance would help raise productivity. Linking education to labour market needs more closely would help improve employment and skills. Greater uptake of digital technologies by firms, along with a modernised public sector and strong skills will also help lift trend growth. Reaching the climate objective of net zero emissions by 2050 will require bold policy action, both on the tax and the spending side.
Company Formation in Lithuania
Lithuania is the biggest of the Baltic states and regards itself as the region’s economic powerhouse. Certainly it has succeeded in attracting significant inflows of foreign direct investment, with investors encouraged by a combination of a stable economy, low inflation, low labour costs and a liberal business environment. Corporation tax is 15%, one of the lowest rates in the EU. Lithuania is one of the most popular locations for business incorporation in northeastern Europe. The business climate in Lithuania is very encouraging. In terms of the nation’s ease of doing business, Lithuania is placed eleventh. It is simple to conduct business in Lithuania because there is only a single stockholder and one director requirement, both of whom can be of any nationality.
The country’s 15% business tax rate is among the lowest in the European Union. Lithuania is one of the most rapidly expanding fintech hubs in Europe, and it is ranked fourth globally. Lithuania, which has a population of about 2.8 million, provides enterprises with a sizable workforce. The service sector made up the majority of the Lithuanian economy, with almost half of the labor force employed in it and accounting for around two-fifths of the country’s yearly GNP.
FAQ Company Formation in Lithuania
What are the main types of company in Lithuania?
- public limited company (AB)
- private limited company (UAB)
- general partnership (TUB) or limited partnership (KUB)
What are the main features of a public limited company?
- minimum share capital is approx. €44,000, at least 25% to be paid up
- one of more shareholders are required in order to register a public company
- auditors required to prepare annual financial statement
- company and its shareholders have limited liability
- you must appoint a supervisory council or “board of management”
What documents are required to register a public limited company?
- the company’s articles of association
- minutes of the founding meeting
- confirmation of Lithuanian bank account
- confirmation of share registration with Securities Commission
- report on company together with auditor’s opinion
What are the main features of a private limited company?
- minimum share capital is approx. €2,900
- maximum number of shareholders is 250
- company and its shareholders have limited liability
What documents are required to register a private limited company?
- the company’s articles of association
- minutes of the founding meeting
- confirmation of Lithuanian bank account
What are the main features of a partnership?
- general partnerships have unlimited liability
- limited partnerships have limited liability
What are the main features of a branch or representative office?
- ranch office can conduct trade within scope set by parent
- representative office can promote but cannot trade
- at least one manager must reside in Lithuania
- no formal auditing requirements
Are there financial incentives available?
- tax holidays and tax reductions for companies investing over €1 million
- no taxes on dividends paid on foreign investments
How much does it cost to set up a company in Lithuania?
What taxes are paid by Lithuanian companies?
And what about banking facilities?
Establishing a business requires careful planning. Working with our experts can help streamline this process, providing valuable insights and tailored strategies to ensure successful outcome. Don’t hesitate any longer. Apply to become a client today to work with our experts on legal strategies to overcome barriers.